EV DICTIONARY | The Comprehensive Guide to EV Jargon—Version 1!
If you are coming from the world of ubiquitous LS engine swaps, turbo boost, and ignition timing, all the electric vehicle jargon being thrown around recently might leave your head spinning. This confusion is completely understandable as electric powertrains are a completely different beast than their fire-breathing counterparts. However, regardless of your background, the intoxicating torque delivery of electric motors should be an option for all of us, no matter how much some of us cling to the smell and price of gasoline.
Let us take the head-scratching out of the equation for you and break down some common EV terms and acronyms.
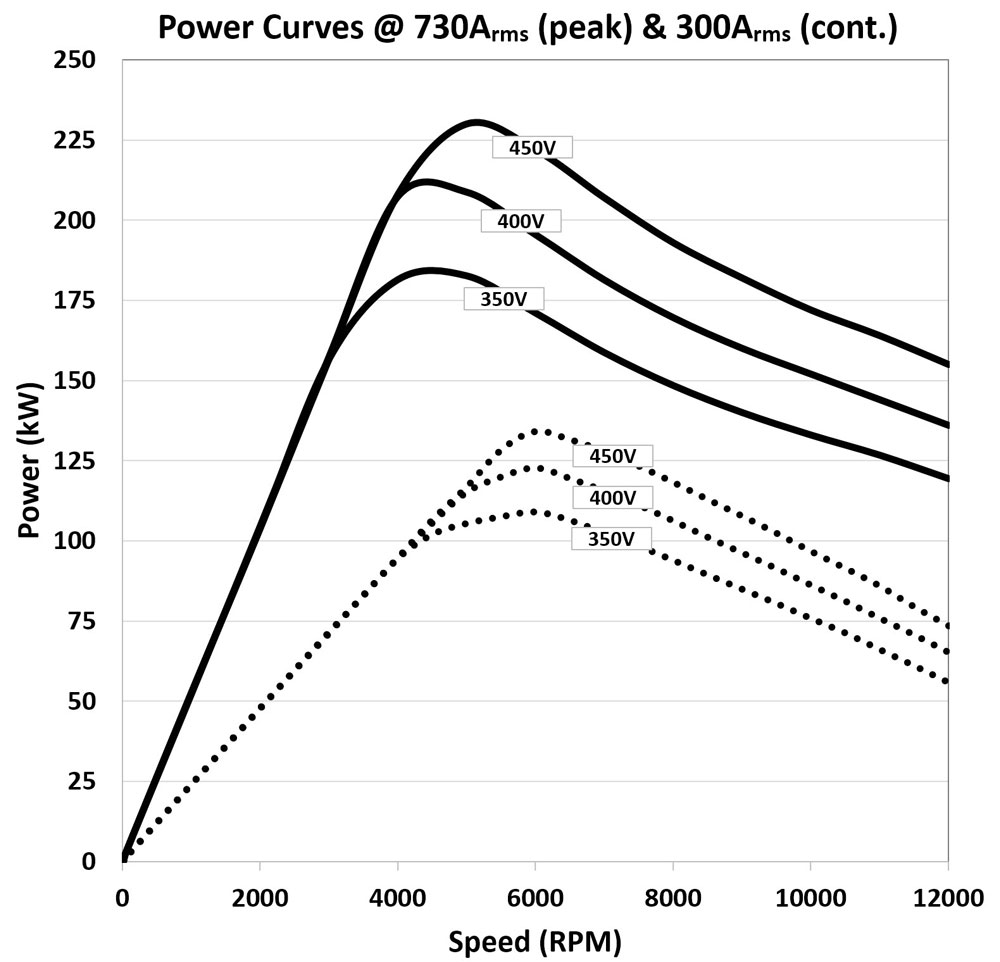
kW
kW stands for kilowatts and is a measure of total power available in an EV. To convert from kilowatts to horsepower simply multiply kilowatts by 1.34. Many EV systems will have two values of kilowatts, peak and continuous. Continuous kilowatts is the amount of power an EV can put down indefinitely. Peak kilowatts is the amount of power an EV can produce under maximum load situations such as maximum acceleration.
BMS
An acronym for Battery Management System. A BMS is a way to monitor and control battery pack health to ensure performance, safety, and long-term reliability. A BMS uses wires known as cell taps to monitor the individual battery cells in series and communicate with other systems accordingly

OBC
An acronym for Onboard Battery Charger. An OBC converts AC electrical power to DC power to charge the large battery pack in an EV.

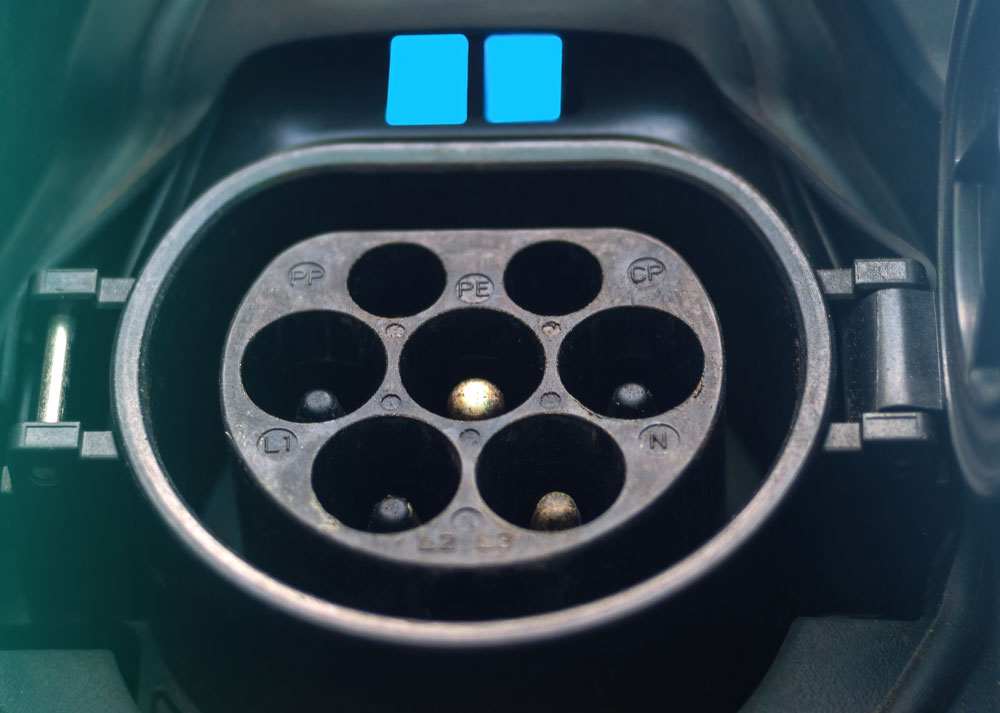
EVSE
An acronym for Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment. An EVSE supplies electric energy to recharge electric vehicles. This is also known as a charging station and can likely be found at your local college campus, natural grocery store, and luxury apartment complex. Given the current trends, in time EVSEs will be as common as gas stations.

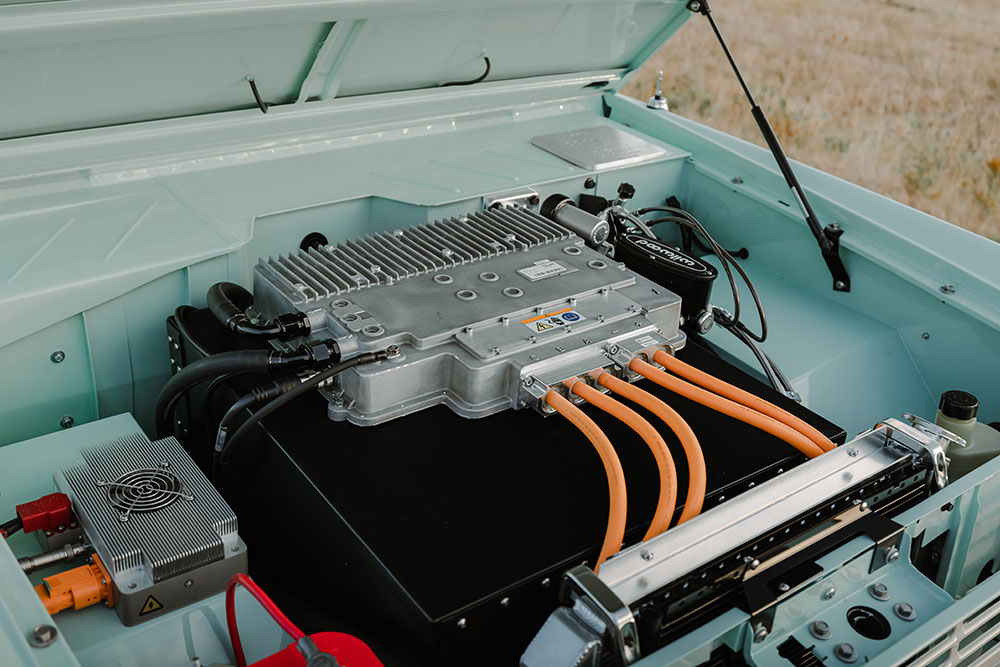
Inverter
Electric vehicles use inverters to take the high-voltage, high-current DC electric power found in EV battery packs and convert it to AC power for the EV’s motor(s). AC power provides the best control of speed and torque in an electric vehicle.
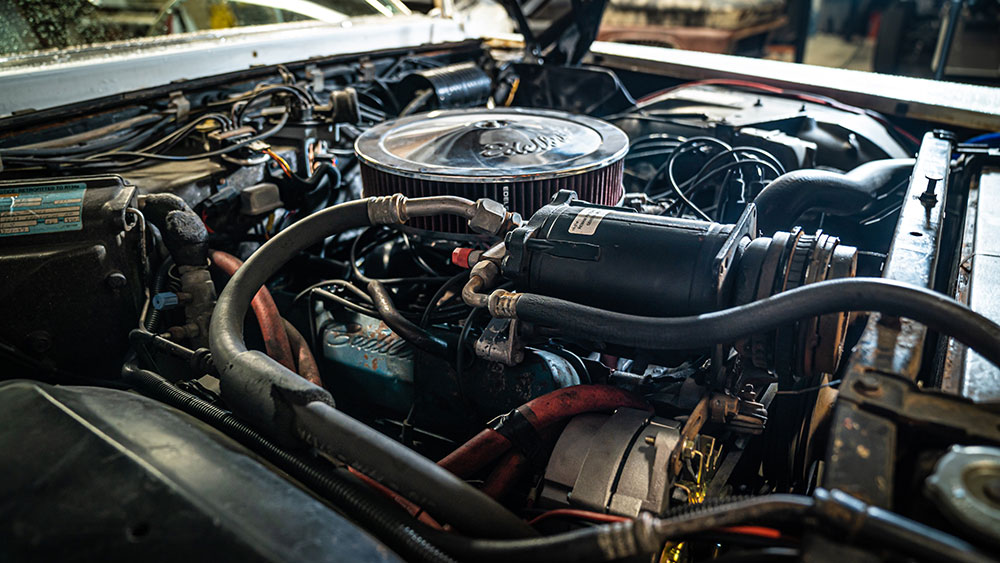
ICE
An acronym for Internal Combustion Engine. ICE is a convenient and efficient way to lump all gas and diesel engines together. If it burns fossil fuels to provide power to the wheels, it’s an ICE.
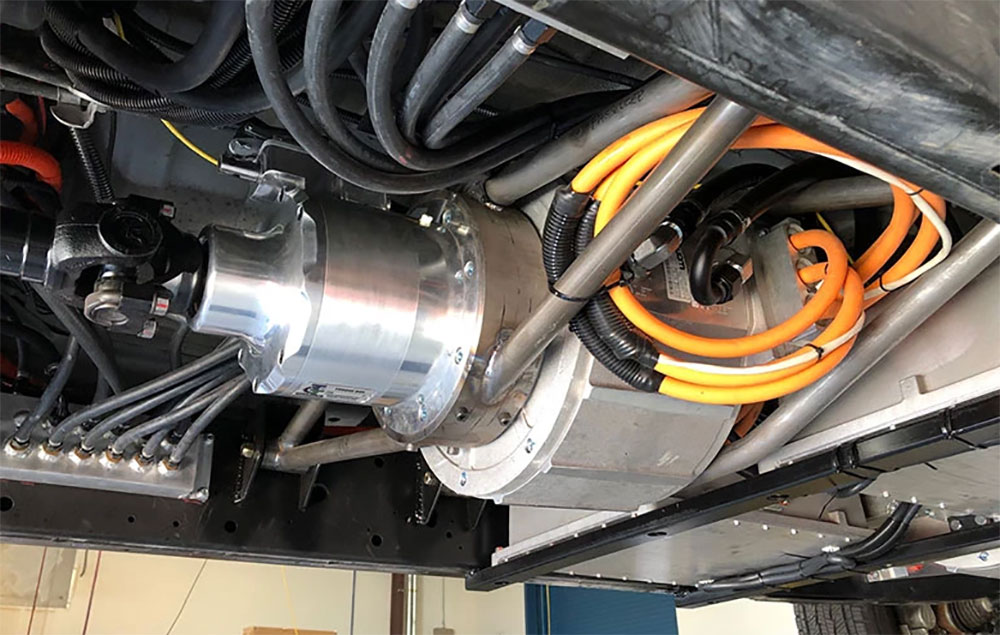
Direct Drive
Electric motors put out enough torque throughout every step in their rev range that most don’t need multi-gear transmissions. Instead, they use direct drive, which is often coupled with gear reduction for optimal performance.

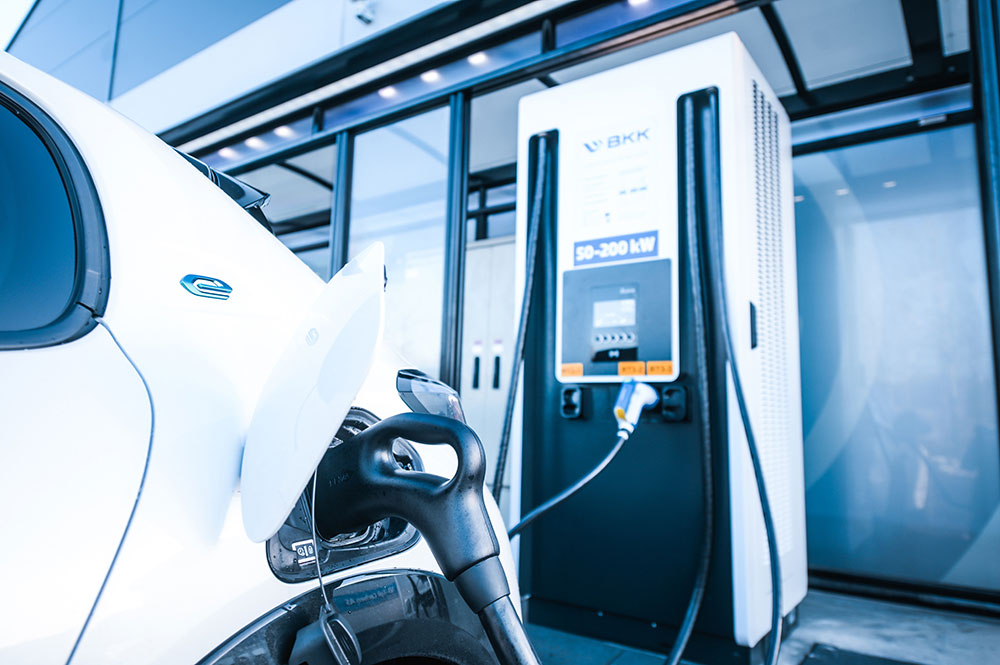
DC Fast Charging
DC fast charging is the fastest way to charge electric vehicles with an output ranging from 50kW to 120kW. Depending on the battery pack size, DC fast charging can fully charge an electric vehicle in an hour or less. DC fast charging is sometimes referred to as Level-3 charging, however this a misnomer as there is no level officially classified as Level-3.

Level-2 Charging
Level-2 charging supplies 240 volts to the battery charger. Faster than Level-1 charging, but slower than DC fast charging, this is the most common charging type available.
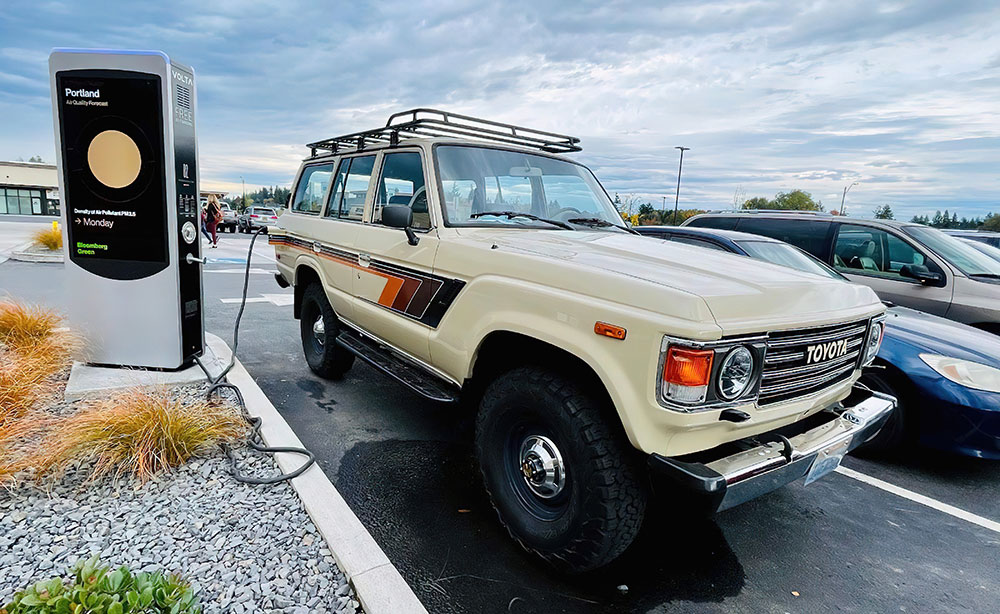

Level-1 Charging
Level-1 charging supplies 120 volts to the battery charger and is the slowest charging type available.

kWh
EV battery pack size is often measured in kWh or kilowatt hour. A kilowatt hour is the amount of electrical energy consumption of 1,000 watts for one hour.

Miles per kWh
Miles per kWh is a measurement of an electric vehicle’s efficiency and is determined by a wide range of factors including vehicle aerodynamics, powertrain efficiency, driving conditions, and more.

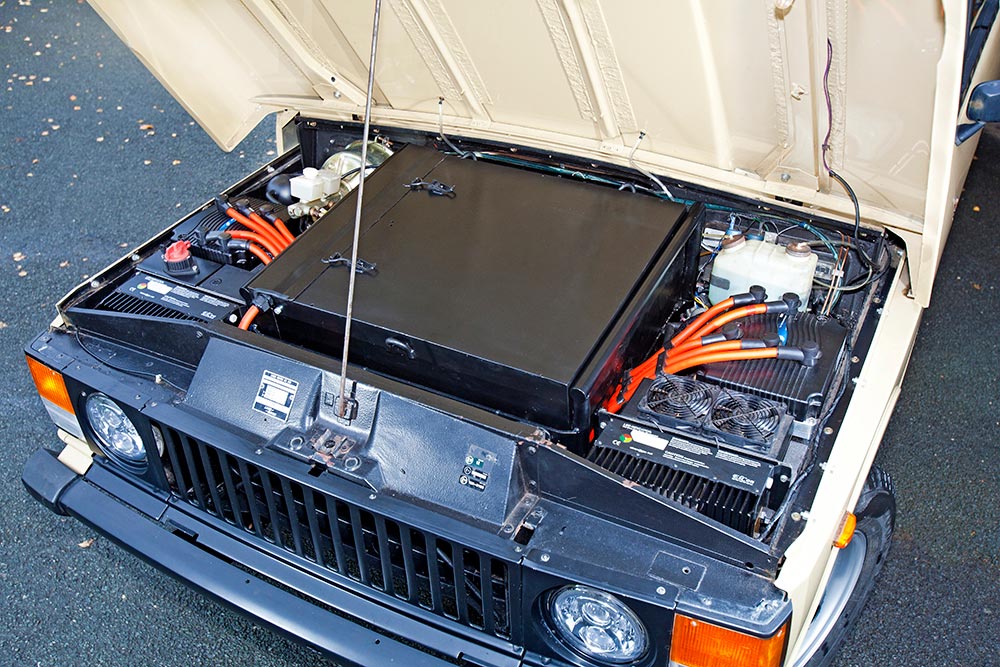
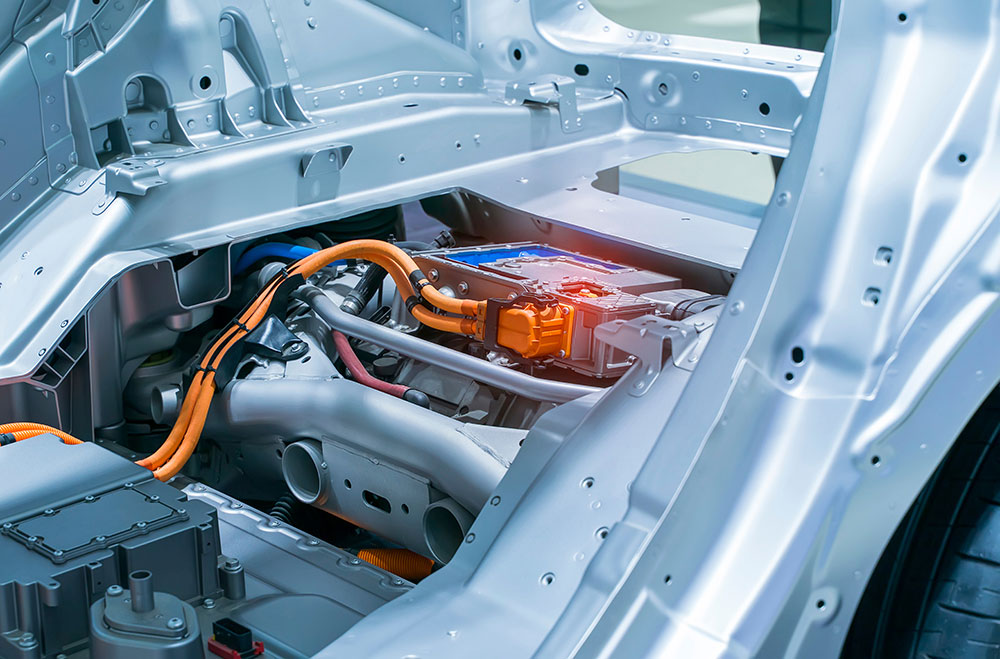
Battery Pack
A battery pack is the power-storage component in an EV. A battery pack is a configuration of battery cells designed to hit target voltage and current draw required by the EV motor. It also includes the battery management system and, in some cases, the thermal management devices.
MPGe
MPGe stands for “miles per gallon gasoline equivalent” and represents the amount of miles an electric vehicle is estimated to be capable of traveling on the equivalent amount of energy contained in a gallon of gasoline.












